Economy Overview and Key Drivers
When you think about economy, the system of production, distribution, and consumption that shapes a country’s wealth and living standards. Also known as economic system, it forms the backdrop for every business decision and policy move.
The manufacturing, the process of turning raw materials into finished goods sector sits at the heart of this system. A robust manufacturing base fuels job creation, boosts export earnings, and feeds downstream services. In India, cities like Surat dominate textile output while states such as Gujarat lead electronics exports – real examples that illustrate how manufacturing propels the overall economic engine.
But no economy runs in a vacuum. A recession, a period of declining economic activity across the economy can quickly erode growth, cut consumer spending, and stall investment. During downturns, industries that rely heavily on discretionary spending feel the pinch first, while essentials like pharma and basic goods hold steadier ground. This is why many companies chase recession‑proof niches – they act as a buffer that keeps the larger economic picture from collapsing.
Another pillar is trade, the exchange of goods and services between countries or regions. International trade lets manufacturers access bigger markets, source cheaper inputs, and scale faster. India's rank in global electronics manufacturing, for instance, rose thanks to strong export ties with the US and Europe. At the same time, trade policies and tariffs directly influence domestic pricing, affecting everything from furniture costs to pharma drug availability.
All these threads – manufacturing, recession dynamics, and trade flows – weave together to shape the broader economy. Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that break down each piece: how IKEA’s supply chain works in India, the rise of Cipla in pharma, why Surat leads the textile world, strategies for recession‑proof businesses, and the impact of India’s single‑use plastic ban on manufacturing. Dive in to see real data, practical tips, and the latest trends that define today’s economic landscape.
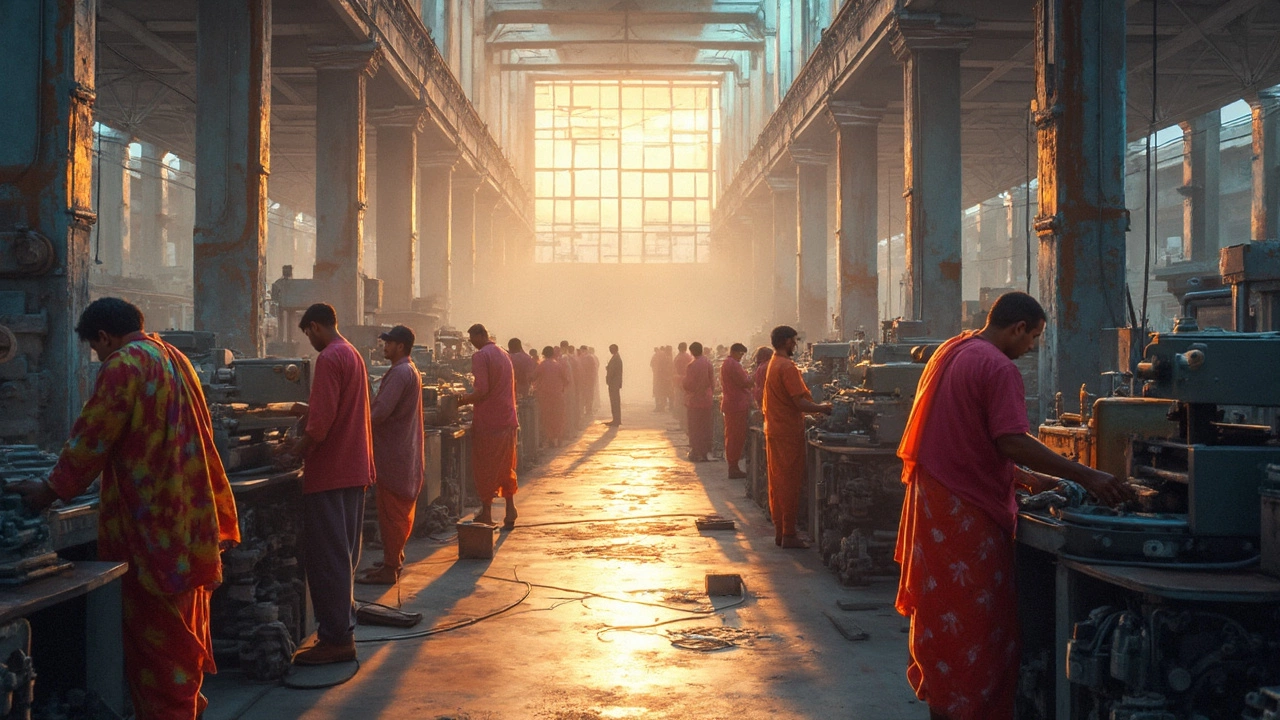

Manufacturing plays a crucial role in boosting the economy by creating jobs, fostering innovation, and driving exports. From enhancing supply chains to offering potential tax incentives, government schemes often aim to support this vital sector. By producing goods domestically, countries reduce dependency on imports and improve trade balances. Understanding why and how manufacturing impacts economic growth can help in making informed policy decisions. This article delves into the various ways manufacturing benefits the economy. (Read More)