Production Processes: The Engine Behind Indian Manufacturing
When working with production processes, the ordered series of steps that turn raw inputs into finished products. Also known as manufacturing workflows, they shape efficiency, cost and quality in every factory. Manufacturing, the broader activity of producing goods at scale depends on well‑designed processes, while supply chain, the network that moves materials from source to plant provides the inputs that keep those steps running. Add material selection, choosing the right raw material for strength, cost and sustainability, and industrial automation, the use of robots and control systems to speed up production, and you have the full ecosystem that powers modern factories.
Production processes are the backbone of any successful operation because they link design, resources and final output. A well‑planned process reduces waste, shortens lead times, and boosts product consistency. In India, companies are tightening these links to meet global standards while keeping costs low. For example, a furniture maker might integrate CNC cutting (automation) with locally sourced teak (material selection) and a regional logistics partner (supply chain) to deliver a premium product faster than competitors.
Key Elements of Effective Production Processes
First, clear process mapping is essential. Mapping shows where each operation sits, what tools are needed, and how quality checks fit in. Second, material selection cannot be an afterthought; choosing the right alloy, wood grade or polymer influences durability and price. Third, a resilient supply chain provides the right parts at the right time – a single delay can halt an entire line. Fourth, industrial automation adds speed and precision, especially in high‑volume sectors like textiles or electronics. Finally, continuous improvement loops, such as Kaizen or Six Sigma, ensure the process evolves with market demands and new technology.
Understanding these connections helps you see why a change in one area ripples through the whole system. When a factory upgrades its automation, it often reassesses material specs and renegotiates supplier contracts to keep the workflow smooth. Likewise, a shift to sustainable materials may require new quality checks and altered logistics routes.
The articles below dive deeper into each of these topics – from the nitty‑gritty of material choices for Indian furniture to real‑world supply‑chain case studies in the pharma sector. Explore the collection to see how production processes shape the future of Indian manufacturing.
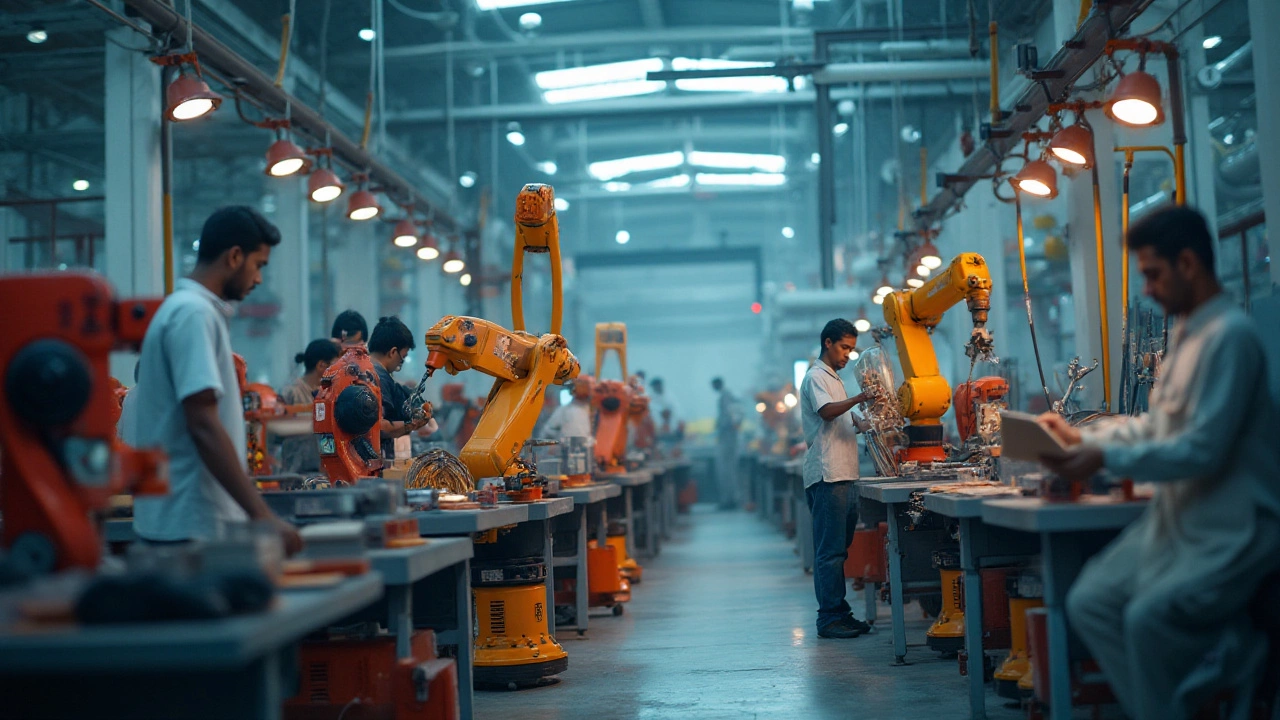

Manufacturing in 2025 is witnessing significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing global demands. The two main types of manufacturing processes are discrete and process manufacturing, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these types is crucial for businesses to optimize production and make informed decisions about government schemes that support industrial growth. This article delves into the intricacies of these manufacturing types, offering insights into their mechanisms, advantages, and how they align with government initiatives. (Read More)